Fabric Zoning for the IBM Spectrum Virtualize and FlashSystem NPIV Feature
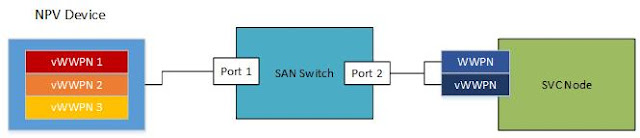
Zoning Basics Before I talk about some zoning best-practices, I should explain two different types of zoning and how they work. There are two types of zoning: WWPN Zoning and Switch-Port Zoning World-wide Port Name (WWPN) Zoning WWPN zoning is also called "soft" zoning and is based off the WWPN that is assigned to a specific port on a fibre-channel adapter. The WWPN serves a similar function as a MAC address does on an ethernet adapter. WWPN-based zoning uses the WWPN of devices logged into the fabric to determine which device can connect to which other devices. Most fabrics are zoned using WWPN zoning. It is more flexible than switch-port zoning - a device can be plugged in anywhere on the SAN (with some caveats beyond the scope of this blog post) and the device can connect to the other devices it is zoned to. It has one distinct advantage over Switch-Port based zoning, which is that zoning can always be specified on a single WW...






